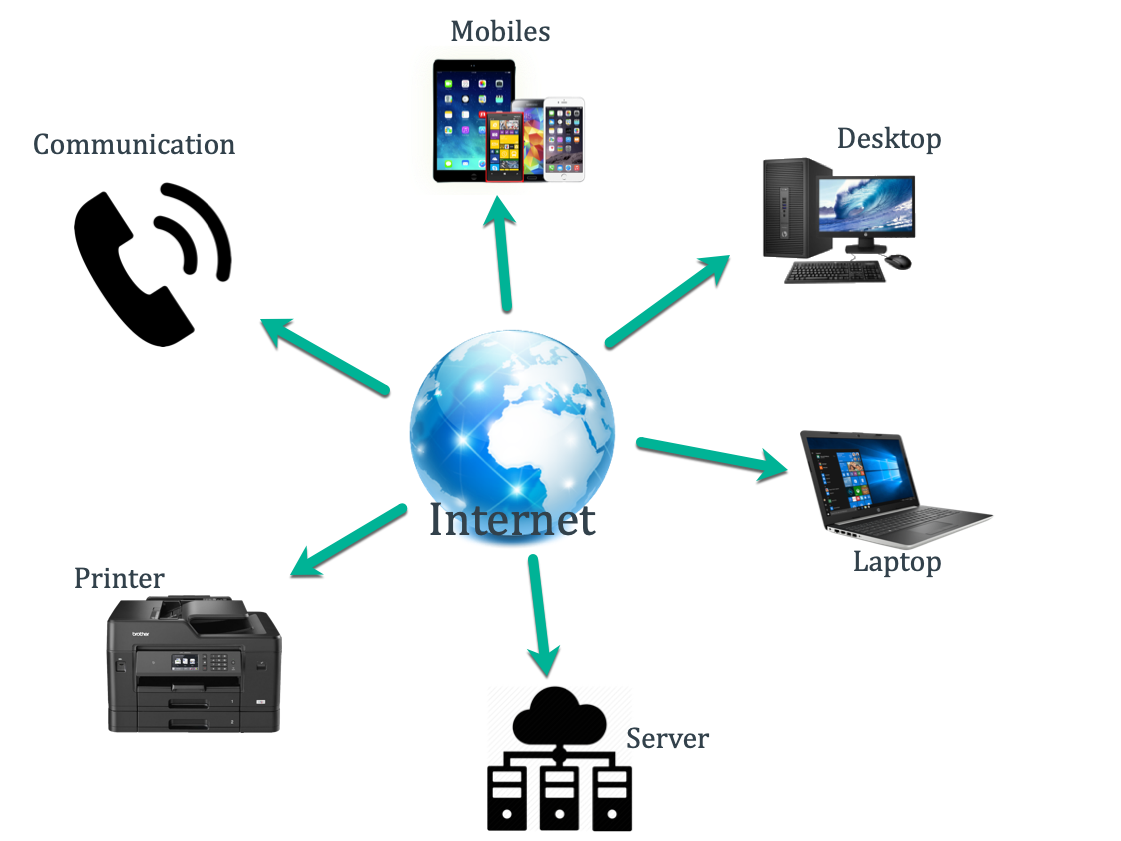
Internet
The internet, short for "interconnected networks," is a global network of computers and computer networks that are connected and communicate with each other using a standardized set of protocols. It is a vast infrastructure that allows people, organizations, and machines to share and access information, resources, and services across geographical distances.
-
Information Sharing
It serves as a vast repository of information on practically any subject. Websites, blogs, online encyclopedias, and other platforms host information that can be accessed by users worldwide.
-
Information Sharing
It serves as a vast repository of information on practically any subject. Websites, blogs, online encyclopedias, and other platforms host information that can be accessed by users worldwide.
-
Education
Educational resources and courses are available online, enabling distance learning and self-paced education.
Key Features of the Internet
Global Connectivity
One of the most fundamental features of the internet is its ability to connect people, devices, and networks from around the world.
Information Access
The internet is a vast repository of information on virtually every topic imaginable.
Multimedia Content
The internet offers a diverse range of multimedia content, including streaming videos, music, podcasts, and interactive media.
Search Engines
Search engines like Google, Bing, and others make it possible to quickly find relevant information by entering keywords or queries.
E-commerce and Online Shopping
Businesses can set up online stores, allowing consumers to browse, shop, and make purchases from the comfort of their homes.
Online Education and E-Learning
The internet has transformed education by offering online courses, tutorials, and educational resources.
Cloud Computing
Cloud services allow users to store and access data, applications, and resources remotely over the internet.
Digital Innovation and Startups
internet has lowered barriers to entry for startups and innovators, allowing them to reach a global audience and disrupt traditional industries.
Broadband
Broadband refers to high-speed internet access that provides a substantial amount of data transmission capacity. It enables faster and more reliable internet connections compared to traditional dial-up connections, which were much slower. Broadband technology allows for the simultaneous transmission of various types of data, such as voice, video, and data, over a single connection.

-
Broadband connections enable users to engage in bandwidth-intensive activities such as streaming high-definition videos, online gaming, video conferencing, and downloading large files more efficiently. The term "broadband" signifies the ability to transmit a broad range of frequencies, which allows for the simultaneous transmission of various types of data.
-
Overall, broadband has significantly transformed how people use the internet by providing faster and more versatile connections that support the demands of modern online activities.
-
A broadband plan refers to a subscription package or service offering provided by an internet service provider (ISP) that outlines the terms, conditions, and features of your internet connection.
Broadband Plan
Broadband plans are designed to meet various needs and preferences, offering different speeds, data limits, and additional services. Here are some key aspects typically found in a broadband plan:
Download and Upload Speeds
Broadband plans specify the speed at which data can be downloaded and uploaded. Speeds are measured in megabits per second (Mbps) and indicate how quickly you can access and transmit data over the internet.
Data Allowance
Many broadband plans have a data allowance, which determines how much data you can use within a billing cycle. Some plans offer unlimited data usage, while others have specific data caps. Exceeding the data limit may result in additional charges or reduced speeds.
Connection Type
The plan will specify the type of broadband connection you'll have, such as DSL, cable, fiber optic, satellite, or wireless.
Contract Duration
Some broadband plans require you to commit to a contract for a specific duration, such as 12 months or 24 months. Other plans might offer month-to-month options without a long-term commitment.
Monthly Cost
The plan will outline the monthly fee you'll need to pay for your broadband service. Costs can vary based on factors like speed, data allowance, and additional services.
Additional Services
Broadband plans might include additional services like a Wi-Fi router, security software, email accounts, and customer support.
Bundle Options
Some ISPs offer bundle packages that include not only broadband but also other services like TV, phone, or mobile plans.
Peak and Off-Peak Times
Some plans have different data allowances or speeds during peak usage hours (when many people are online) and off-peak hours.
Installation and Setup
The plan may detail any fees associated with installation, setup, or equipment rental.
Availability
Broadband plans are often tied to specific geographic areas. The plan will indicate whether the service is available in your location.
Customer Support
The plan might outline the customer support options available to you, including phone, email, and online resources.
Cancellation Policy
If you need to cancel the plan before the contract term is over, the plan will specify any cancellation fees or procedures.
Leased line
A leased line, also known as a dedicated line, private line, or data line, is a symmetric telecommunications line that is rented for exclusive use between two locations. It provides a dedicated and continuous connection between these locations, ensuring reliable and consistent data transfer rates. Leased lines are often used by businesses and organizations that require high-speed, reliable, and secure connectivity for their operations.
Leased lines are commonly used for various purposes, such as:
-
Connecting geographically distant office locations within a company's private network.
-
Supporting voice over IP (VoIP) systems for high-quality voice communication.
-
Facilitating video conferencing and real-time collaboration.
-
Transmitting large volumes of data, such as backups or data replication between sites.
Hosting private servers or running online applications that require consistent performance.
.png)
Key Characteristics of leased lines include:
-
Dedicated Connection
Unlike regular internet connections where bandwidth is shared among multiple users, a leased line offers a dedicated and uncontested connection between the two endpoints. This means the full bandwidth of the line is available at all times, ensuring consistent and predictable performance.
-
Symmetric Bandwidth
Leased lines typically offer symmetric bandwidth, meaning the upload and download speeds are the same. This is different from many residential broadband connections that offer higher download speeds than upload speeds.
-
Reliability
Leased lines are known for their high reliability. They are often used for critical applications that require minimal downtime, such as business operations, online transactions, and communication systems.
-
Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Leased line services often come with SLAs that define the guaranteed uptime, performance, and response times for repairs in case of any issues. SLAs help ensure a certain level of quality and availability for the leased line service.
-
Scalability
Leased lines can be scaled up or down to accommodate changing bandwidth needs. This flexibility allows businesses to adjust their connectivity as their requirements evolve.
-
Data Security
Leased lines provide a dedicated connection that is not shared with other users, enhancing the security of data transmission. This makes them suitable for transmitting sensitive information.
-
Point-to-Point Connection
Leased lines establish a direct point-to-point connection between two locations. This can be used for connecting office branches, data centers, or other remote sites.
-
Cost
Leased lines are generally more expensive than standard broadband connections due to their dedicated nature and higher reliability.
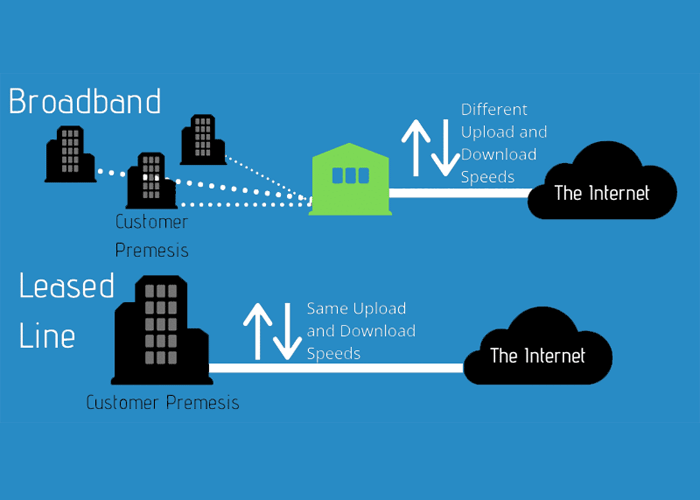
Broadband vs Leased Line
Ut possimus qui ut temporibus culpa velit eveniet modi omnis est adipisci expedita at voluptas atque vitae autem.
-
Broadband and leased lines are two distinct types of internet connections, each with its own set of characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.
-
Here's a comparison between the two: 1 Dedication 2 Speed and Bandwidth 3 Reliability 4 Cost 5 Use Cases.
-
In summary, the choice between broadband and a leased line depends on your specific needs and budget. Broadband is cost-effective and suitable for everyday internet usage, while leased lines are a premium option that offers dedicated, reliable, and high-speed connectivity for businesses and organizations with demanding network requirements.
"Point to Point" (P2P)
-
"Point-to-point" (P2P) refers to a type of communication or connection where data, signals, or information is exchanged between two specific endpoints or devices. This means that information flows directly from one point to another without involving intermediary devices or routing through a network. Point-to-point communication is commonly used in various applications where a direct and secure connection between two specific locations or devices is required. While it has its advantages in terms of simplicity and security, it may not be the most efficient or scalable solution for all types of communication, especially when dealing with large networks or complex data routing requirements.
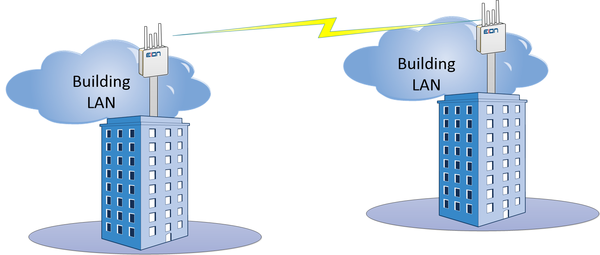
Types of P2P
Fiber Optical P2P
-
Broadband and leased lines are two distinct types of internet connections, each with its own set of characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages.
-
Here's a comparison between the two: 1 Dedication 2 Speed and Bandwidth 3 Reliability 4 Cost 5 Use Cases.
-
In summary, the choice between broadband and a leased line depends on your specific needs and budget. Broadband is cost-effective and suitable for everyday internet usage, while leased lines are a premium option that offers dedicated, reliable, and high-speed connectivity for businesses and organizations with demanding network requirements.
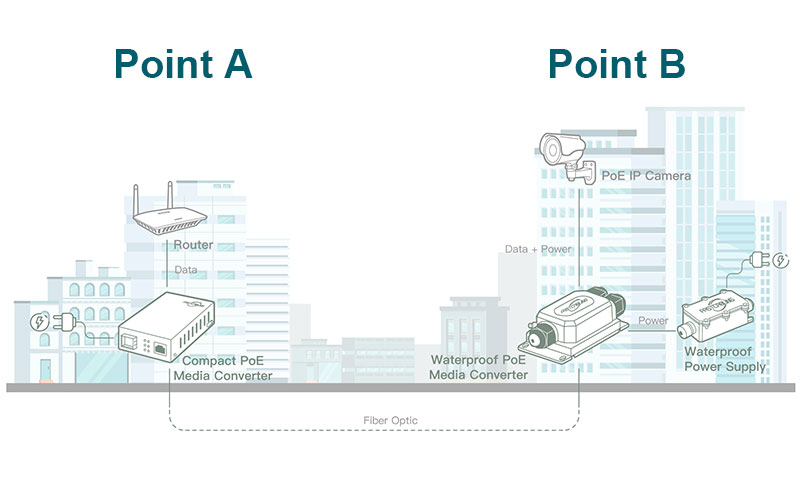
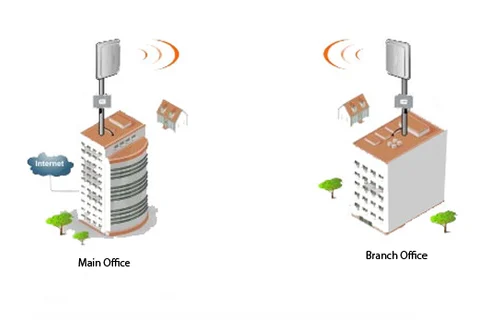
Wireless Point to Point
-
Internet Connectivity: Wireless Internet Service Providers (WISPs) often use point-to-point links to deliver internet access to remote or underserved areas.
-
In urban areas or corporate environments, point-to-point links are used to connect two buildings without the need for expensive and time-consuming cable installations.
-
Point-to-point links can be used to connect security cameras at remote locations to a central monitoring station. This is useful for surveillance and security purposes.

